Difference between revisions of "WiDig-801 QuickStart Windows"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
Also, we need to route the BLE MIDI port to a virtual MIDI port, hence the need for loopMIDI. | Also, we need to route the BLE MIDI port to a virtual MIDI port, hence the need for loopMIDI. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the WiDig is running [[WiConnect]] 1.1xx, [[Connect]] can communicate with the WiDig via USB while it is communicating via BLE. If running [[WiConnect]] 1.0xx on the WiDig, [[Connect]] is not useful as it cannot communicate with the WiDig while it is operating in BLE mode. The Connect software is only able to connect to devices via USB or "Classic" Bluetooth (ie. not BLE). | ||
| + | |||
====Pairing the WiDig==== | ====Pairing the WiDig==== | ||
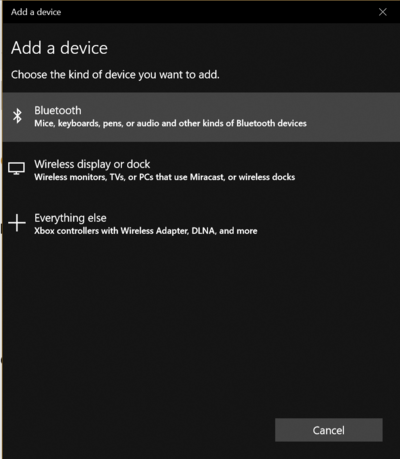
| − | Go to system Settings->Bluetooth & Other Devices, and click on add: | + | '''1.''' Go to system Settings->Bluetooth & Other Devices, and click on add: |
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
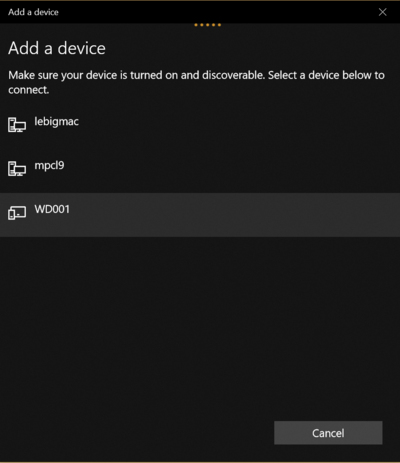
| − | Then, select the WiDig device: | + | '''2.''' Then, select the WiDig device: |
| Line 29: | Line 32: | ||
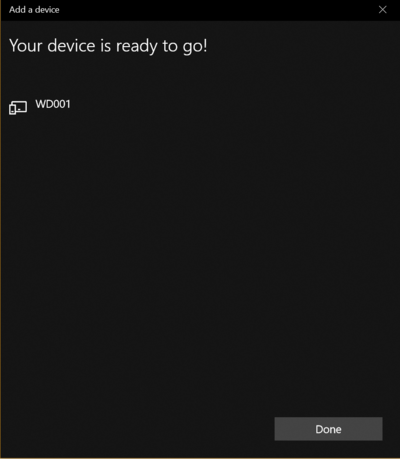
| − | Connect to the device (If it fails once, try again and eventually it should connect): | + | '''3.''' Connect to the device (If it fails once, try again and eventually it should connect): |
| Line 35: | Line 38: | ||
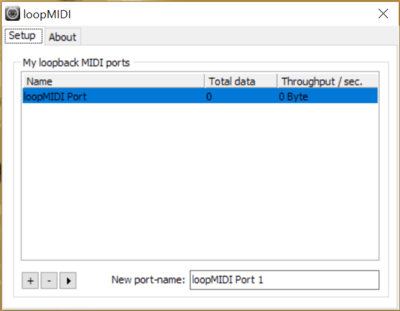
| − | Make sure loopMIDI is running and there is at least one virtual port available: | + | '''4.''' Make sure loopMIDI is running and there is at least one virtual port available: |
| Line 41: | Line 44: | ||
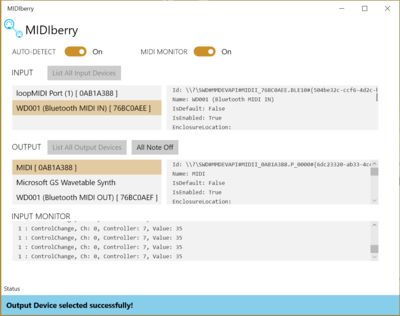
| − | Finally, open MIDIBerry and select the WiDig as input, and the "MIDI" virtual device as output. | + | '''5.''' Finally, open MIDIBerry and select the WiDig as input, and the "MIDI" virtual device as output. |
Now, you will be able to access WiDig sensor data from any MIDI application via the virtual loopMIDI port! | Now, you will be able to access WiDig sensor data from any MIDI application via the virtual loopMIDI port! | ||
Latest revision as of 12:41, 31 August 2021
WiDig BLE on Windows
On Windows, configuration of the WiDig must be done through USB, or using the WIDI Bud adapter, as these communication methods allow both sending and receiving of messages to/from the WiDig.
To only receive sensor data with a generic BLE interface once it is configured in Standalone mode with EditorX (via USB or using a WIDI Bud), the computer must run Windows 10 or higher.
You will need:
- A WiDig configured in Standalone mode, and USB power source
- loopMIDI virtual MIDI application
- MIDIBerry BLE to MIDI bridge application (Windows 10 only)
Also, we need to route the BLE MIDI port to a virtual MIDI port, hence the need for loopMIDI.
If the WiDig is running WiConnect 1.1xx, Connect can communicate with the WiDig via USB while it is communicating via BLE. If running WiConnect 1.0xx on the WiDig, Connect is not useful as it cannot communicate with the WiDig while it is operating in BLE mode. The Connect software is only able to connect to devices via USB or "Classic" Bluetooth (ie. not BLE).
Pairing the WiDig
1. Go to system Settings->Bluetooth & Other Devices, and click on add:
2. Then, select the WiDig device:
3. Connect to the device (If it fails once, try again and eventually it should connect):
4. Make sure loopMIDI is running and there is at least one virtual port available:
5. Finally, open MIDIBerry and select the WiDig as input, and the "MIDI" virtual device as output.
Now, you will be able to access WiDig sensor data from any MIDI application via the virtual loopMIDI port!